How Digital Camera Work as Optical Sensor
Technology Overview
In digital cameras, the data collection method is quite different from analog cameras. Conventional cameras use a chemical reaction to take an image, then emulsify it so that the image appears on film.
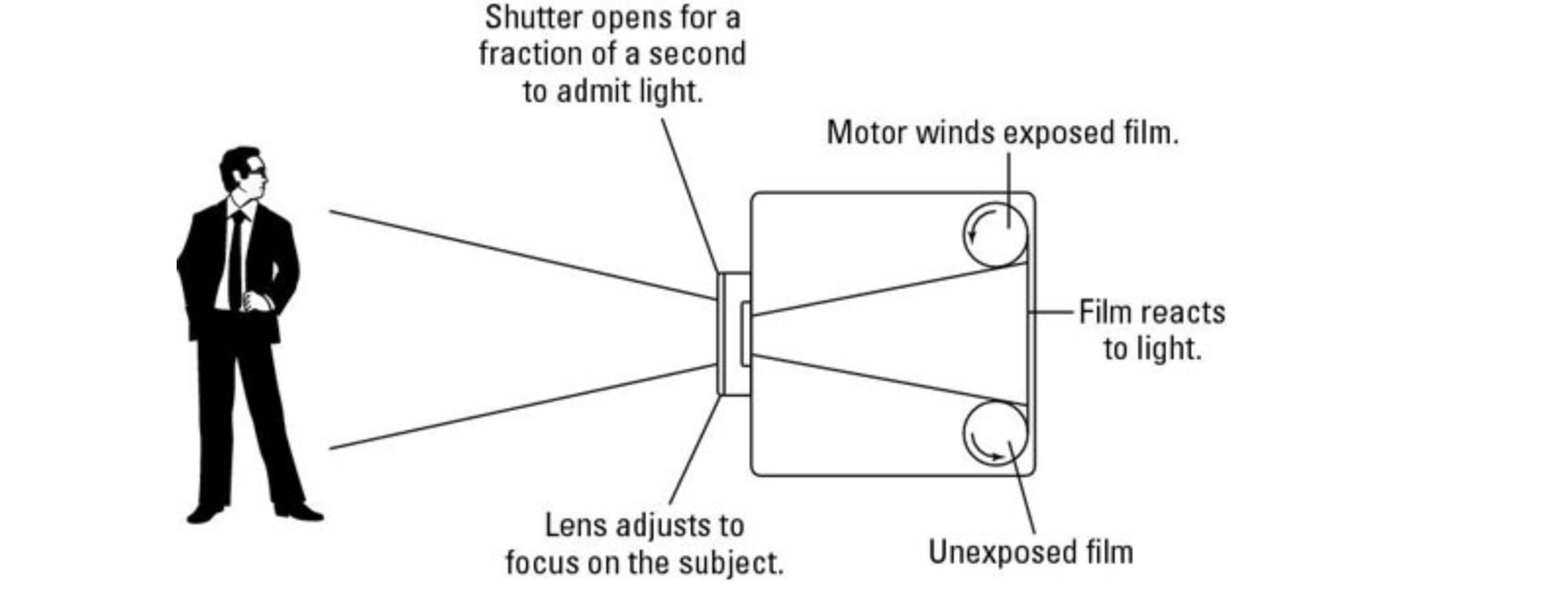
While digital cameras use electronic sensors to retrieve spatial data on variations in light intensity, then use an image processing algorithm to reconstruct the color of the image received by the sensor. There are two technologies in the manufacture of image sensors, namely CCD (Charge Coupled Device) and CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor).
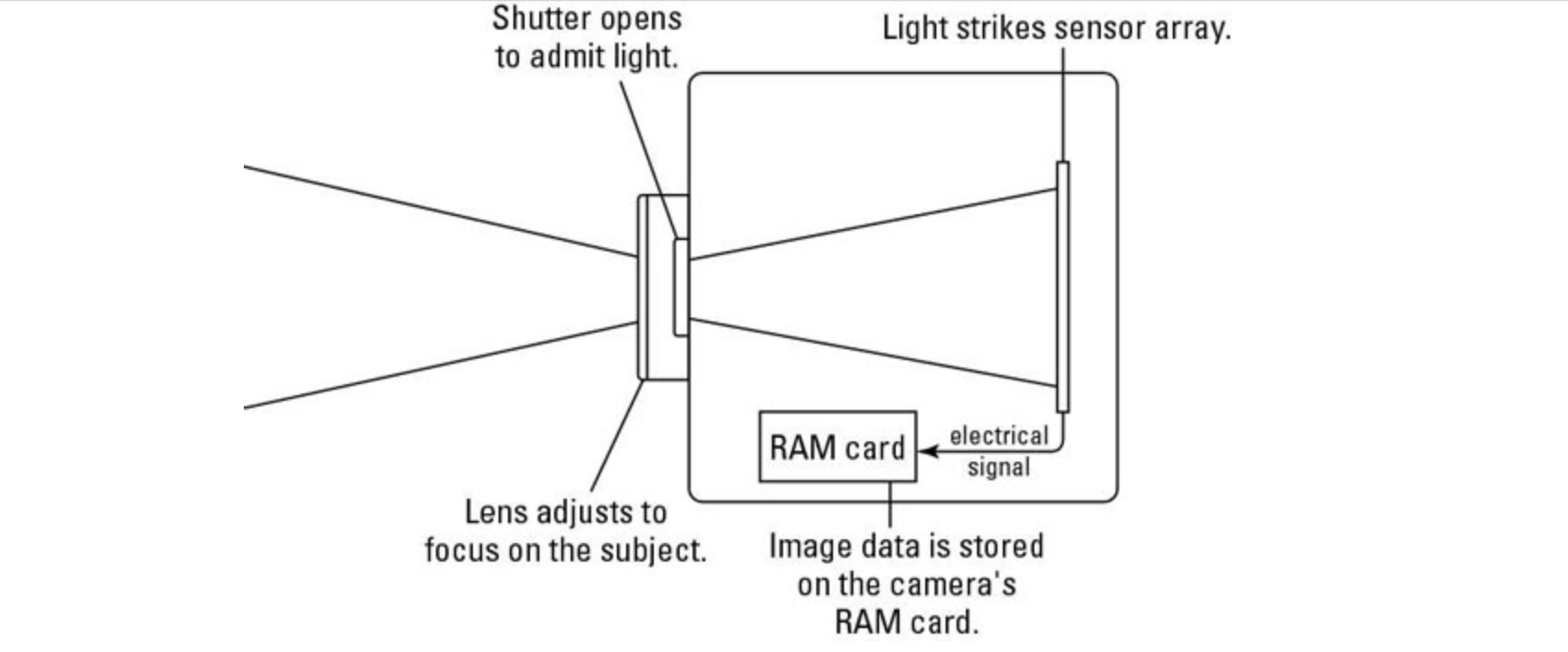
Nowadays and in the future there will be more use of CMOS cameras although CCD cameras will still be used in high-end cameras such as in astronomical observations.
Charged Couple Device (CCD) Camera
At the beginning of its invention the CCD camera in 1970 was invented in 1970 by Boyle and Smith. CCD cameras use light sensitive diodes that convert light in the form of photons into an electric charge in the form of electrons. These diodes are called photosites. Each photodecetor is sensitive to light, the greater the intensity of the incoming light, the greater the accumulated electric charge. Each photodetector is made with a thin layer of silicon dioxide coated with a Polysilicon Gate which is given a positive electrical potential to create a depletion region that stores electrons when the photon beam comes to the sensor. In the real world, the potential wells in photo detectors can reach a million electrons using only a few micrometer depths of the depletion layer.
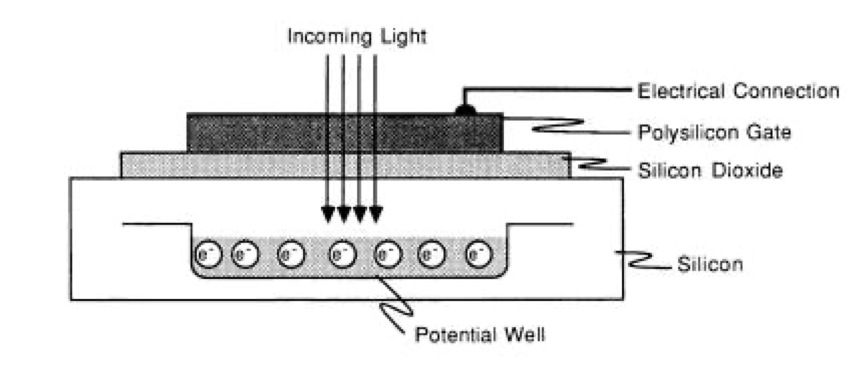
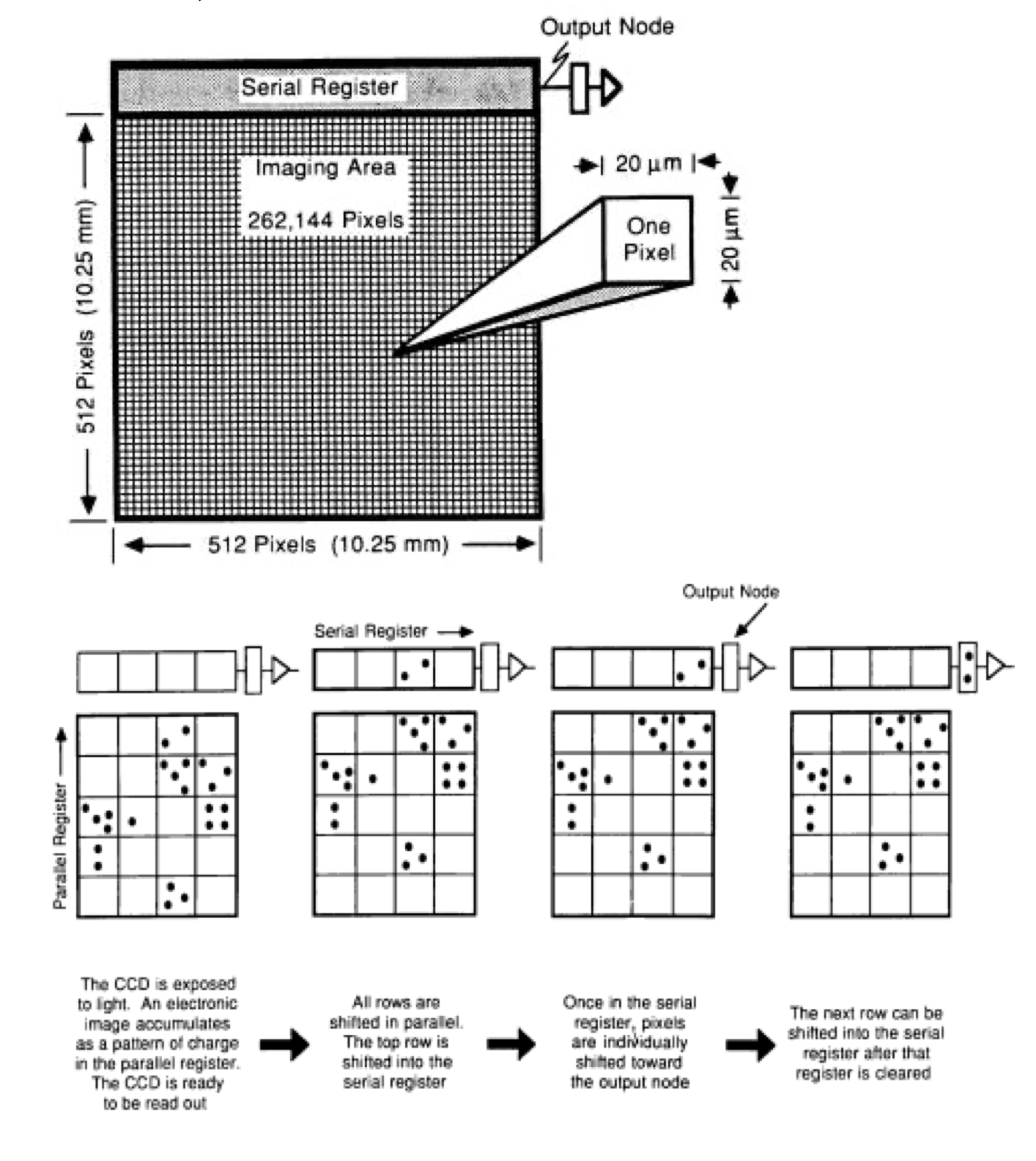
How the charge transfer works on the CCD sensor is illustrated in the image below, namely the electric charge is buried in the conduit under the silicon. Then the transferred load will be distributed to the grid columns on the CCD so that it can be digitized by an ADC (analog to digital converter).
The CCD camera has several sources of noise or interference in the image, namely Dark Current, pixel unevenness, photon collision noise and CCD read noise. The cause of the Dark Current is the temperature produced by the electrons. The variability of pixels is due to the fact that the photodetector on the grid has a different sensitivity to the light signal it receives generally 1% to 2%. Then, Shot Noise because the incoming photons cannot be predicted. The advantages of CCD compared to other camera sensors are about 80% in quantum efficiency, small noise, High Dynamic Range (HDR), High Photometric Precision, very linear work, small voltage required (5-15 Volts only) and the image is geometrically stable so that very suitable when this type of camera is used in astronomical instruments. In fact, the hugely popular Hubble telescope uses a CCD in its image capture sensor.
The invention of the CCD in this image capture led Boyle and Smith to win the Nobel Prize in physics 40 years after its discovery in 2009.

Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) Camera
CMOS cameras use a photodetector that is almost the same as a CCD camera, only on a grid CMOS camera sensor that converts light in the form of photons to an electric charge, each sensor pixel also converts the charge into a voltage signal, while in CCD, the electric charge is first transferred to the output node to be used. convert into a voltage difference signal.
Another difference is that the CMOS sensor also includes other frames such as a digital controller to control each pixel on the sensor grid and ADC. In the picture below illustrates the difference in how the electron charge is converted into a different signal output voltage on the CCD and CMOS sensors.
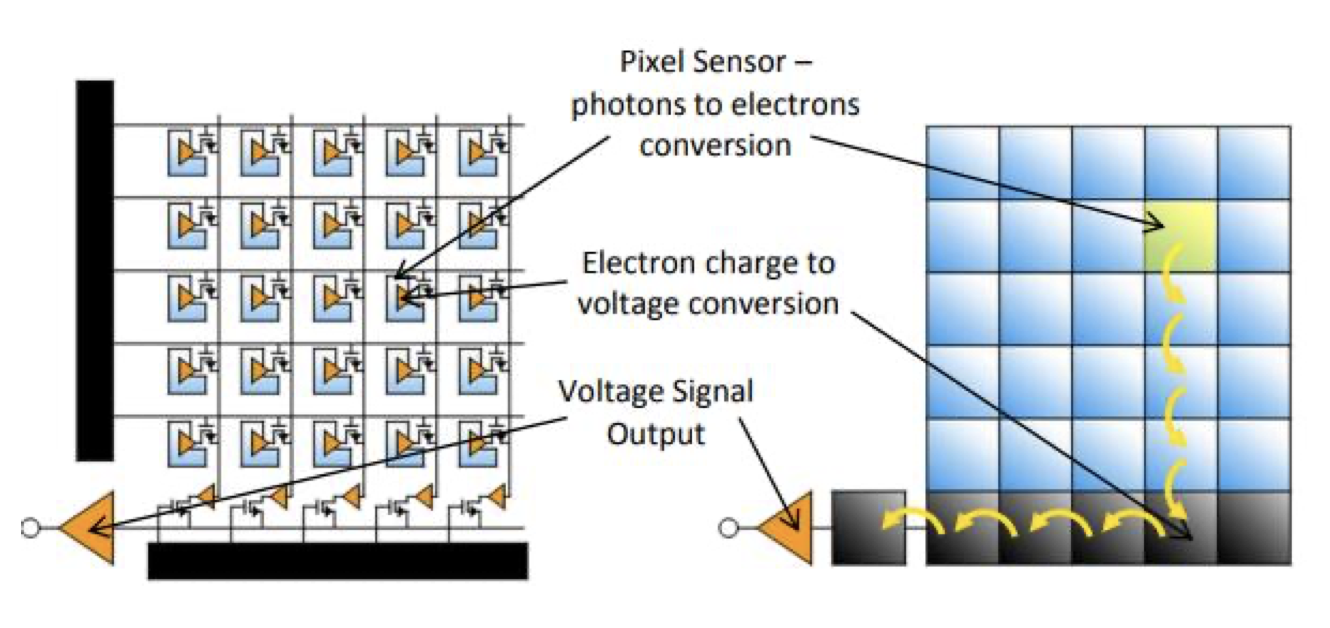
CMOS vs CCD
The table below summarizes the technical differences between CMOS and CCD cameras.
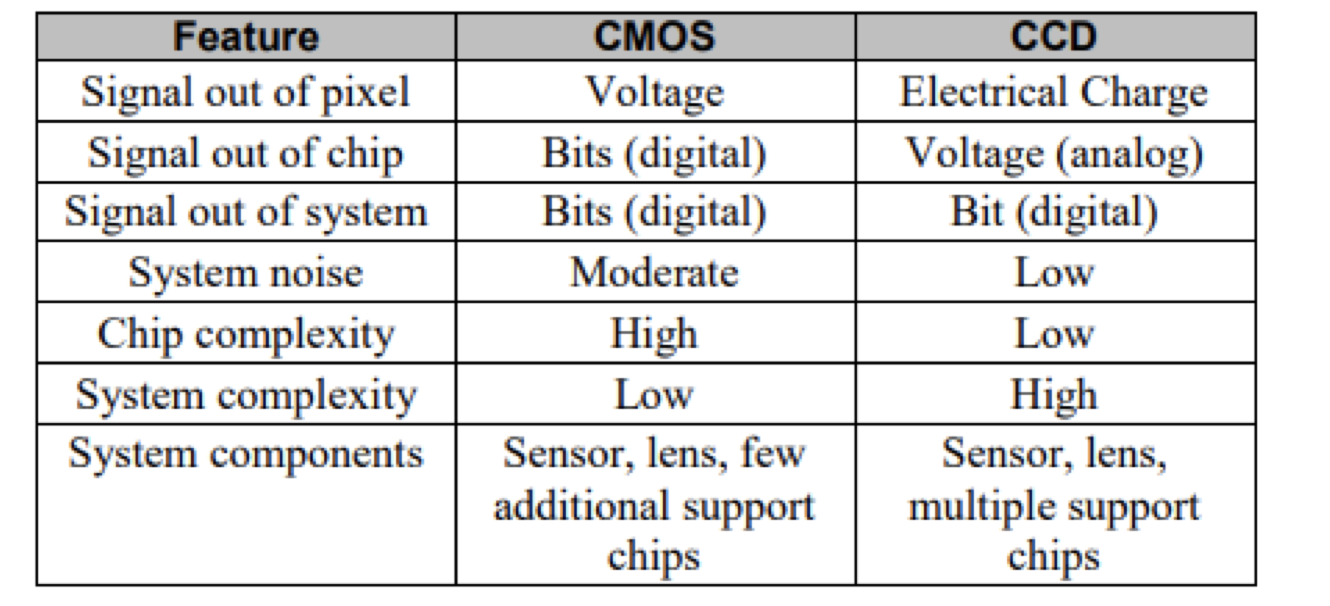
Practically, these two sensors have differences that can be felt directly by the user, namely the CMOS sensor has a lower pixel uniformity than the CCD due to the pixel grid design of the sensor itself. So that images taken by CMOS cameras will generally have greater noise than images taken by CCD cameras. On the production price side, CMOS sensors will be lower than CCDs because CMOS sensors use the same technology on memory and logic chips. The advantage of a CMOS sensor over a CCD sensor is that the CMOS sensor allows for a much smaller system and uses less power, so that the dominant CMOS sensor is used in cellphone cameras.
CMOS sensor applications are now being used in various industries, for example the automotive industry, security and others. However, CMOS camera sensors do not replace CCD camera sensors because CCD sensors have much better image quality and less noise.